Solution: Pressure Vessel
Solution: Pressure Vessel
Pressure Vessel
In which region do you need this solution?
From the first audit to the periodic audit
-
Start of trial operation – When trial operation is started, an initial operational test by an accredited inspection body must be arranged in accordance with the Pressure Equipment Monitoring Ordinance. This involves a safety assessment of the pressure vessel with regard to its suitability for the intended operation at the installation site.
-
Periodic inspection – Subsequently, pressure vessels must be periodically inspected according to their inspection level assigned by the accredited inspection body. The tests are external inspection, internal inspection and main inspection (consisting of external inspection, internal inspection and water pressure test).
-
Responsibility of the operator – Both the first operational inspection and the subsequent periodic inspections must be arranged by the operator.
-
Alternative to the water pressure test – If a water pressure test is not possible, there is also the option of carrying out an acoustic emission test. In this case, the tank is checked with the help of a computer. This type of examination is possible both as a substitute for an internal examination and as a water pressure test.
-
Inspection by operator in case of low hazard potential – Vessels with low hazard potential are to be inspected by the operator himself, e.g. in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. However, operator testing may also be delegated to an inspection body.
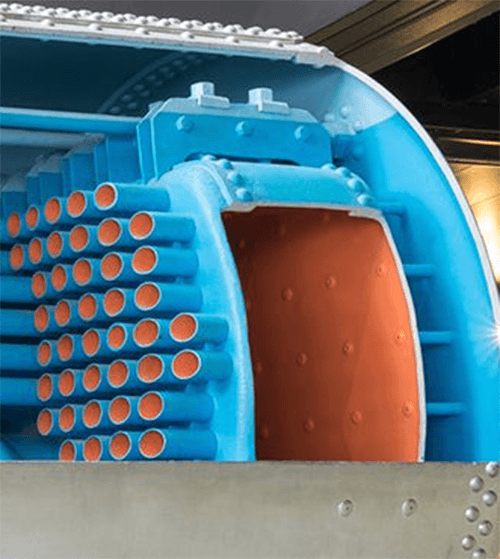
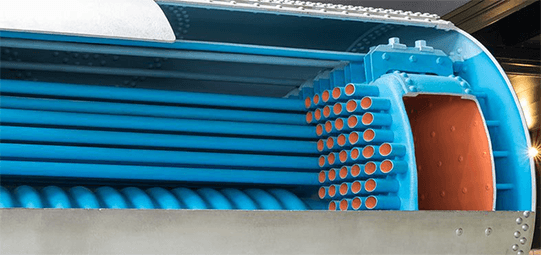
According to the Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU, a pressure vessel is a closed component designed and constructed to contain fluids under pressure. This also includes directly attached parts up to the device for connection to other equipment.
Examples of pressure vessels include compressed air vessels, sandblasting vessels, bladder accumulators, heat exchangers, etc.
Test types |
Time limits |
| First audit | At the start of the trial operation |
| Audit | On resumption of operation after more than one year out of service or change of location |
| Periodic audit | Depending on the inspection level.1) consisting of either an exterior inspection, an exterior and interior inspection or a main inspection (AU/IU/pressure test). |
Inspection intervals for pressure vessels Inspection stage 1
- for the external inspections – 3 years
- for the internal inspections – 12 years
- for the pressure tests – 12 years
Inspection intervals for pressure vessels Inspection stage 2
- for the external examinations – 1 year
- for the internal examinations – 3 years
- for the pressure tests – 9 years
Inspection intervals for pressure vessels Inspection stage 3
- for the first external examination – 1 year
- for the subsequent external examinations – 1 to 5 years
- for the first internal examination – 1 year
- for the subsequent internal examinations – 1 to 5 years
- for the first pressure test – 2 years
- for the subsequent pressure tests – 2 to 10 years
Inspection intervals for pressure vessels Inspection stage 4
- for the external examinations – 2 years
- for the internal examinations – 6 years
- for the pressure tests – 12 years