Solution: Penetrant Testing (PT)
Penetrant Testing (PT)
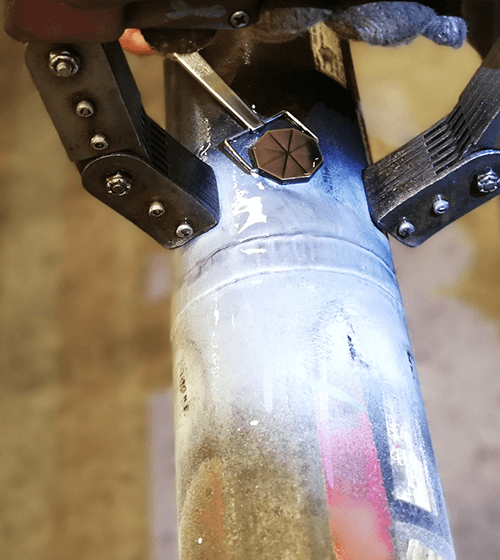
Penetrant testing is a non-destructive materials test that uses the capillary action of fine surface cracks and pores to make them visible. This means that the defects must be open to the surface. A distinction is made between dye penetrant testing and fluorescent penetrant testing.
Dye penetrant testing
Dye penetrant testing involves removing grease and oil residues from the surface of the component to be tested and then applying a penetrant. This can be done by application with a brush, by dipping or, in well-ventilated locations, by spraying. The penetrant has a high creep capacity, uses the capillary action of the finest material separations and it has a strong color contrast with the developer.
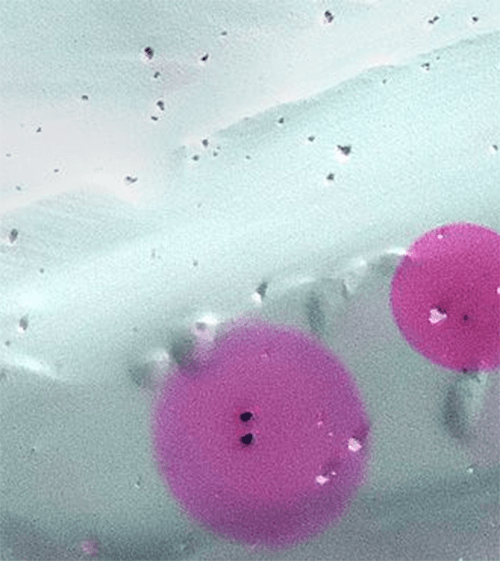
After the penetrant time, which depends on the material to be tested, has elapsed, the surface is cleaned with water or a special cleaner, dried and the developer is applied. The developer is a fine-grained powder (usually lime-based, suspended in water or solvent) which, through the capillary action of its own cavities (absorbency), draws out the penetrant remaining in the fine cracks or cavities. Usually, the penetrant (dye solution) is red and the developer is white. The high color contrast allows easy localization of defect locations and determination of the indication gradients.
Area of application
Dye penetrant testing is suitable for finding cracks or voids in the surface of a material very easily and quickly. However, so-called false indications can occur on rough or brittle surfaces. These indications are not defects. The method also does not allow any statement to be made about the depth of the defect in relation to the intensity of the indication.
Fluorescent indentation testing
In low ambient light conditions, fluorescent penetrant can be used, which can be made visible by UV irradiation. This test is much more sensitive than dye penetrant testing because the fluorescent particles create a luminance contrast by converting UVA radiation into visible light. People are much more sensitive to luminance contrasts than to color contrasts.
Application area
This indentation test can be used on all materials that allow clear indication of surface defects (are not porous). In the case of steel components, a solvent-based developer is usually used because of the high susceptibility to corrosion by water.